Typescripte基础知识
定义原始数据类型
null和undefined是所有类型的子类型。可以复制给任何类型let arrOfNum: number[] = [1, 2, 3, 4]; // 定义元素类型为数子的数组tuple元组类型let user: [string, number] = ['jolly', 30]; // 两项,第一项类型为 string, 第二项类型为 number函数声明
// 指定参数类型和返回值类型
function add(x: number, y: number, z?: number): number{
return x + y;
}
let add2 = (x: number, y: number, z?: number): number => {
return x + y;
}
let add3: (x: number, y:number) => number = add2;Type inference 类型推断
let s = 'str'; // s 类型判定为 'string'. 不能被赋值为非 'string' 类型的值。
interface
- 定义对象类型及形状
interface Person {
readonly id: number,
name: string,
age?: number
}
// 合法代码
let jolly: Person = {
name: 'jolly',
age: 30,
id: 1 // id不能被修改
}
- 定义函数类型
interface Count {
(x: number, y: number): number // 定义参数类型和返回值
}
const sum: Count = (x: number, y: number) => x + y;
- Indexable type 可索引类型
interface Randmap {
[propName: string]: string;
}
const map: Randmap = {
a: 'a',
b: 'b',
c: 'c' // 合法
// d: 1 // 不合法,期望 String
}
- LIke Array 类型
interface LikeArray {
[index: number]: string
}
const likeArray: LikeArray = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
likeArray[0]; // 只能访问,没有其他方法
- duck typing 鸭子类型
// 定义一个四不像
interface FunWithProps {
(x: number): number;
name: string;
}
const a: FunWithProps = (x: number) => { // 传入类型要为 number
// return 'x' // 不合法,返回类型应为 number
return x
}
a.name = 'adf' // 类型要为 string
类和接口
publicprivate- 只在实例上可以访问,子类上不能访问
protected- 只在子类上可以访问,实例上不能访问
- interface 约束类,implements 实现类
interface ClockInterface {
currentTime: number,
alert(): void
}
interface GameInterface {
play(): void
}
// 合法代码
class Cellphone implements ClockInterface, GameInterface {
currentTime: number = 123;
alert() {
}
play() {
}
}
interface 约束构造函数
类的类型由两部分组成:
- 静态类型,这个类本身的类型
- 实例类型,使用
new关键字创建的实例的类型
构造函数由约束静态类型,从而得到约束
// 约束静态类型
interface ClockStatic {
new (h: number, m: number): void;
time: number
}
// 约束实例类型的属性方法
interface ClockInterface {
currentTime: number,
alert(): void
}
// 约束实例类型的属性方法
interface GameInterface {
play(): void
}
const Cellphone: ClockStatic = class Cellphone implements ClockInterface, GameInterface {
constructor(h: number, m1: number){
}
static time: 12
currentTime: number = 123;
alert() {
}
play() {
}
}
泛型
函数和泛型
泛型解决的问题
类型推断不能延伸到函数
- 泛型是在定义函数和接口的时候,不预先指定类型,而在使用时指定类型的一种特性
function echo<T>(arg: T): T {
return arg; // T 是泛型的名称,可随意起名。可以理解为将来由参数类型替代
}
const result = echo('str'); // result 类型为 string。T = string
// 泛型可以传入多个值
function swap<T, U>(tuple: [T, U]): [U, T] {
return [tuple[1], tuple[0]];
}
//
泛型和接口
从 react 定义文件学习 泛型和接口
安装 @types/react
使用命令 create-react-app 创建 react 项目,返现并没有 @types/react 于是手动安装
npm i -S @types/react
安装了之后,在 tsx 文件中才能 引入 FunctionComponent 接口,不然会报错 “react 没有导出 FunctionComponent”
用来学习的 ts 源码便是 FunctionComponent 接口的定义
interface FunctionComponent<P = {}> {
(props: PropsWithChildren<P>, context?: any): ReactElement<any, any> | null;
propTypes?: WeakValidationMap<P>;
contextTypes?: ValidationMap<any>;
defaultProps?: Partial<P>;
displayName?: string;
}
例:
import { FunctionComponent } from 'react'
interface TestProps {
title: string,
desc: string
}
// 将接口 TestProps 传递到函数FunctionComponent中
const Test: FunctionComponent<TestProps> = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<h1>{props.title}</h1>
<p>{props.desc}</p>
</div>
)
}
从 react ts 定义文件源码得知
泛型的默认值
<P = {}>类型别名:
typetype PlusType = (x: number, y: number) => number
let sum: PlusType = (x: numver, y: number) => x + y
// WeakValidationMap 的定义
type WeakValidationMap<T> = {
[K in keyof T]?: null extends T[K]
? Validator<T[K] | null | undefined>
: undefined extends T[K]
? Validator<T[K] | null | undefined>
: Validator<T[K]>
};交叉类型 '&'
同时要有两个接口中的定义的数据
interface IName {
name: string
}
type IPerson = IName & { age: number }
let person: IPerson = { name: 'hello', age: 12 } // 同时要有两个接口中的定义的数据
// 源码中定义 PropsWithChildren 类型,用到了
type PropsWithChildren<P> = P & { children?: ReactNode }联合类型 '|' 注意,在
typescript不确定传入的类型是联合类型中的哪种时,我们只能访问两种类型共有的属性和方法。怎样判断是联合类型中的哪种类型,请看后面的 “类型断言”let numberOrString: number | string // numberOrString 为 number 或 string 类型Partial功能,接受一个泛型, 将其中的属性或函数变为可选。是typescript内置类型interface Person {
name: string,
age: number
}
type PersonOptional = Partial<Person>
/*PersonOption = interface {
name?: string,
age?: number
}*/
// Partial 的源码
type Partial<T> = {
[P in keyof T]?: T[P]; // ? 表示可选
};extends
在类型别名
WeakValidationMap的赋值处,出现了extends操作符type WeakValidationMap<T> = {
[K in keyof T]?: null extends T[K]
? Validator<T[K] | null | undefined>
: undefined extends T[K]
? Validator<T[K] | null | undefined>
: Validator<T[K]>
};extends作用是判断一个类型是否满足另一个类型的约束。进行泛型约束
interface IWithLength {
length: number
}
function echoWithArr<T extends IWithLength>(arg: T): T {
console.log(arg.length) // 将来传入的参数中,不一定有length。于是需要 extends 进行约束:传入的之中,必须有 length 属性
return arg;
}条件类型关键字
WeakValidationMap中extends的作用便是条件类型关键字,产生一个条件类型。type NonType<T> = T extends null | undefined ? never : T // 假如泛型参数 T 为 null 或 undefined, 返回 never;否则返回 T
// NonType<T> 变为条件类型:是什么类型,看传入的泛型 T 的类型。
let demo1: NonType<number> // demo1 的类型是 number
let demo1: NonType<null> // demo1 的类型是 never
Partial 的实现
keyof操作符,获取键值in操作符,用作循环
interface CountryResp {
name: string;
area: number;
population: number;
}
// keyof
type keys = keyof CountryResp // keys = 'name' | 'area' | 'population'
// 在 keys 中的取值
type NameType = CountryResp['name']
type CountryOpt = {
[p in Keys]?: CountryResp[p]
}
// CountryOpt = {
// name?: string;
// area?: number;
// population?: number;
// }
// Partial 的源码
type Partial<T> = {
[P in keyof T]?: T[P];
};
常量类型
上面注释中的代码
keys = 'name' | 'area' | 'population''name''area''population'就是常量类型注意下面的代码
const str = '123' // 用const定义常量, str 类型为 '123' 类型
let str1 = '123' // str1 类型是 string
类型断言
使用 as 操作符实现
function getLength(input: number | string) { // 使用了联合类型(ps:一般不要在 '{' 后面写注释,这里只是方便讲解)
const str = input as string // 视为 string 类型
// 通过某个类型特有的属性,判断断言是否成立
if (str.length) {
return str.length
} else {
const number = input as number //
return number.toString().length
}
}
注意,类型断言不是类型转换,如果 as 后面是一个新的类型,将报错
// 我们将上面的代码中的任何一个 as 后面的类型换为未指定类型
const number = input as boolean // 报错:类型 "string | number" 到类型 "boolean" 的转换可能是错误的...
定义文件
用于 ts 编译时的检查,没有实现真正的代码功能
基础
定义文件命名:
xx.d.ts使用
declaredeclare var JQuery: (selector: string) => any;如果 JQuery 是通过
<script>标签引入,不是通过import引入,则以上声明可以使ts不报错npm 包名为 @types/xx 是声明文件
@type/XX包的创建,需要向 DefinitelyTyped 提交定义文件,需要其审批。社区默认情况下,node_modules 下面的 @types 包都会被编译器自动加载
高级用法
编写声明文件
type HTTPMethod = 'GET' | 'POST' | 'PATCH' |'DELETE'
declare function myFetch<T = any>(url: string, method: HTTPMethod, data?: any): Promise<T>
declare namespace myFetch {
const get: <T = any>(url: string) => Promise<T>;
const post: <T = any>(url: string, data: any) => Promist<T>;
}
export = myFetch // 放入 node_modules 后要添加
可以放入一下文件夹中
node_modules
|—— @tayps
|—— myFetch
|—— index.d.ts
现在,在 ts 文件中写 myFatch 方法时,就可一个获得提示了
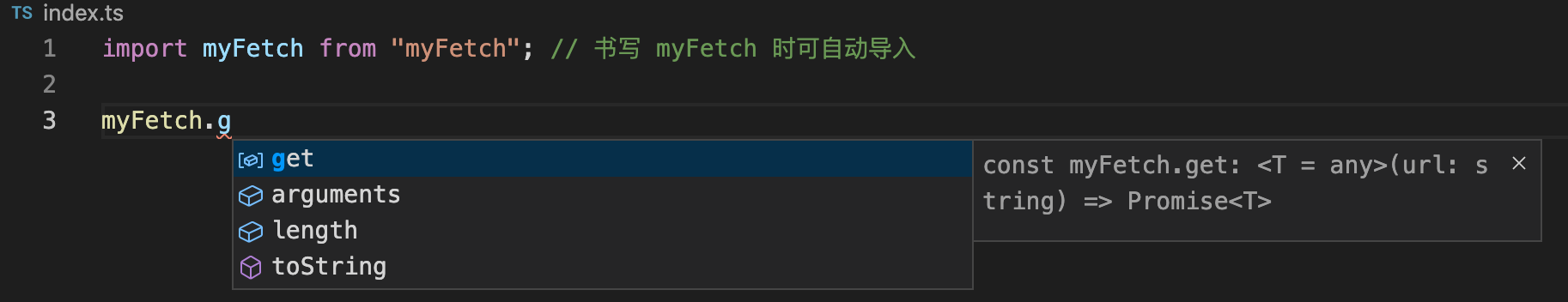 注意:
注意:
- 这样做,只是为了在书写
ts代码时获得良好的提示。实际方法的执行逻辑是没有的,在编译成js执行会报错 import导入的文件,实际上是node_modules/@types/myFetch/index
下面看看,真正使用环境下的目录
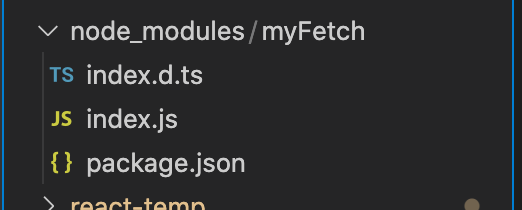 注意:
注意:
ts声明文件的文件名,应和实际的js文件名保持一致(.d.ts是声明文件的固定格式)
知识点总结
- 基本类型
- 类型推断
- interface
- class
- 泛型
reactFunctionComponent定义文件源码- 类型别名
- 联合类型
- 交叉类型
- Partial
- keyof, in
- 常量类型
- extends
- 类型断言
- 编写声明文件
内置类型还包括很多
- Promise ...
学习方法
多看别人的定义文件,尤其是大项目的。